Types of Fuel Cells
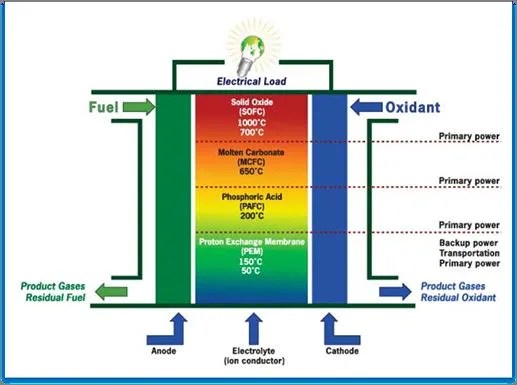
The different types of fuel cells include Alkaline Fuel Cell, Direct Methanol Fuel Cell, Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell, Phosphoric Acid Fuel Cell, Solid Oxide Fuel Cell, and Molten Carbonate Fuel Cell.
Type of Fuel Cell
Operating Temperature (˚C)
Fuel
Electrolyte
Alkaline Fuel Cell (AFC)
40 to 200
Hydrogen
KOH
Direct Methanol Fuel Cell (DMFC)
60 to 130
Methanol
Polymer
Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell (PEMFC)
40 to 90
Hydrogen/ Carbondioxide
Polymer
Phosphoric Acid Fuel Cell (PAFC)
200
Hydrogen/ Carbondioxide
Phosphoric Acid
Solid Oxide Fuel Cell. (SOFC)
600 to 950
Methane, Hydrogen and carbon monoxide
Solid Acid
Molten Carbonate Fuel Cell. (MCFC)
650
Methane, Hydrogen and carbon monoxide
Molten Carbonate
Hydrogen Fuel Cells:
Hydrogen Fuel and air that has oxygen reacts when they come into make contact with an electrolyte that splits them. And this reaction results in the transmission of the electrons and ions across electrolyte from anode to cathode. If the external load is added to this and a complete circuit is created and the voltage is produced from the stream of electrical current.
Efficiency of Hydrogen Fuel Cell:
- 40% efficiency produced, coverts methanol to hydrogen in reformer
- 80% efficiency for motor, converts electrical to mechanical energy
- Overall Efficiency- 24 to 32%
- 80% of hydrogen energy content converted to the electrical energy
Hydrogen @ room temperature:
- Lighter than air
- Colourless
- Easiest and most rich constituent
- Odourless
- More proficient than the current fuels utilised in the transportation
- Additional energy per weight than that of any other energy mediums
Comparison of Auto Power Efficiency:
Technology
System Efficiency
Gasoline Engine
20%
Fuel Cell
24 to 32%
Electric Battery
26%